
Read This On Our Main Website: https://psoec.com/an-ocean-near-you-in-no-time/?feed_id=1061&_unique_id=61b035ab9a4cd
[ad_1]
 By Patricia Burke
By Patricia Burke
Plans for an Internet of Underwater Things and the growing militarization of the oceans, together with using sonar, are accelerating.
As famous in yesterday's article EMF / RF / 5G / Internet Of Underwater Things: Devastation To Whales Warnings, the court docket just lately dominated that the story acquired little mainstream consideration The FCC's decision not to review its radio frequency exposure limits was arbitrary, arbitrary, and not evidence-based. The judgment associated to human publicity limits.
A 3-part detailed examination the environmental impact of non-ionizing radiation additionally just lately appeared in Environmental well being evaluations.
Regulators, engineers, and scientists focusing on the oceans are doing inadequate work to guard humanity from hurt from radio frequency air pollution. We can not prolong these errors to the seas.
Microwave listening to harm
Mainstream tradition and the medical discipline have failed to acknowledge the results of "microwave hearing" perceived exterior of what's referred to as the "hearing range" of the species.
Reports of injury surfaced when people started to "hear" frequencies from the sensible grid, as talked about on "Sandaura's Blog" The worldwide hum is explained and we are all lied to. “Health harm attributable to sensible meters will not be taken under consideration.
Military and industrial researchers recommend that the underwater ecosystem might be protected by figuring out a tolerance degree for noise and utilizing a noise measurement as a dedication for "safety".
Chronobiology is the important thing
Society has failed to acknowledge the distinction between noise that's perceived by way of the sensory organs of listening to, the ears, and “noise” that assaults an organism by way of microwave listening to.
This results in widespread impairment of sleep for people, on account of which immunity is impaired. Rather than being harmonized by and with the planet's altering frequencies that choreograph all physiological capabilities from digestion to the wake and sleep cycle, chronobiology itself is topic to widespread disruption and air pollution.
Take Control Of Your Family Health - Immune System Support Kit (Advertisement)
 We can not prolong these cognitive errors to the oceans.
We can not prolong these cognitive errors to the oceans.
Sound within the oceans is way more advanced than sound within the air - channeling
NOAA explained:
How far does sound journey within the ocean? The distance that sound travels within the ocean varies broadly and relies upon primarily on the water temperature and strain.
While sound strikes a lot sooner in water than in air, the gap that sound waves journey relies upon totally on the temperature and strain of the ocean. While the strain continues to extend with growing sea depth, the temperature of the ocean solely decreases as much as a sure level after which stays comparatively secure. These components have a curious impact on how (and the way far) sound waves journey.
Imagine a whale swims by way of the ocean calling for its pod. The whale creates sound waves that transfer like waves in water. As the whale's sound waves journey by way of the water, their pace decreases with growing depth (with reducing temperature), which breaks the sound waves downwards. As quickly because the sound waves attain the underside of the so-called thermocline layer, the pace of sound reaches its minimal. The thermocline is a area characterised by speedy temperature and strain adjustments that happen at varied depths all over the world. Below the thermocline "layer" the temperature stays fixed, however the strain continues to rise. This will increase the pace of sound and the sound waves are refracted upwards.
The "sound channel"
The space within the ocean the place sound waves break up and down is named the “sound channel”. By channeling sound waves, sound can journey hundreds of kilometers with out the sign dropping any vital quantity of vitality. In reality, hydrophones or underwater microphones, when positioned on the appropriate depth, can decide up whale songs and synthetic sounds from miles away. - NOAA
Marine noise air pollution
July 2021 Marine Pollution Bulletin Reports,
"Underwater noise within the ocean and its results on marine animals is a vital world nature conservation situation (Duarte et al., 2021).
Underwater noise has a wide range of results on marine life, together with acoustic masking (Clark et al., 2009; Erbe et al., 2016), Behavioral problems (Gomez et al., 2016; Nowacek et al., 2007; Southall et al., 2007), elevated stress hormone ranges (Rolland et al., 2012), Hearing loss (Finneran, 2016; Southall et al., 2019) and even demise (McCauley et al., 2017).
The results of underwater noise have been studied most in marine mammals (Gomez et al., 2016; Southall et al., 2007, Southall et al., 2019) and had been additionally examined on fish (Cox et al., 2018; de Jong et al., 2020; Slabbekoorn et al., 2010) and invertebrates (McCauley et al., 2017; Murchy et al., 2020).
Specific Species Sensitivities - Land-Based Research
“Species Sensitivity to a Global Pollutant: A Meta-Analysis of Acoustic Signals as a Response to Anthropogenic Noise"Noted:" Anthropogenic environmental changes are affecting our planet on an unprecedented scale. These changes include changes in the acoustic environment caused by anthropogenic noise, which can affect both animals and humans. In many species, acoustic communication plays a crucial role in maintaining social relationships through the exchange of information via acoustic signals. However, it is still poorly understood how species that rely on acoustic communication differ in their adaptations to anthropogenic noise. This is vital, however, as conservation effectively depends on our ability to predict how species will differ in their response to human-made environmental changes. Using a phylogenetically controlled meta-analysis, we quantified differences in the adaptation of acoustic signals to anthropogenic noise between species. The effect sizes included in the analysis were obtained from noise exposure experiments, since only carefully controlled experiments allow cause-effect relationships to be established. We found that animals changed acoustic cues when exposed to noise, but the strength and direction of the adaptations varied between species. Given the importance of communication in the animal kingdom, these adaptations can affect social relationships in many species. The diversity of inter-species responses underscores the need to assess the impact of environmental stressors on more than a few species, as one impact may be positive for one species but negative for another, depending on the species' biology. Therefore, an effective conservation approach to protecting various species is to preserve natural soundscapes from ecosystems to which the species have adapted Reducing or reducing the emission of anthropogenic noise into the environment.”
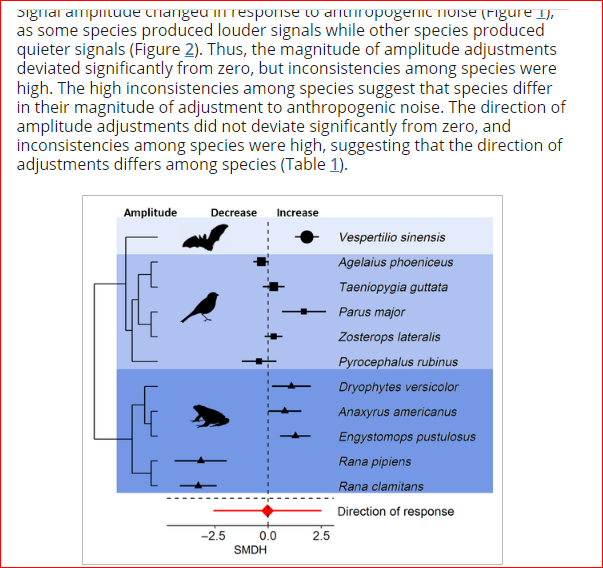 In their conclusion, the researchers notice;
In their conclusion, the researchers notice;
“Animals that had been experimentally uncovered to anthropogenic noise tailored their acoustic alerts. Given the significance of communication all through the animal kingdom, noise has the potential to have an effect on social relationships amongst people of many species. We discovered completely different response patterns between species inside function parts, underscoring the necessity to unravel the mechanisms underlying why species differ of their sensitivity to human-made environmental adjustments. The completely different response between species has vital implications for legislative our bodies to allow efficient conservation: It is solely not sufficient to evaluate the results of environmental stressors similar to noise on the premise of some species, since uniform laws doesn't assure efficient species safety attributable to completely different species sensitivities. Conservation has historically been involved with sustaining biodiversity and the habitats on which organisms rely. Given the results of noise on animals in all taxa, pure soundscapes to which the species have tailored are crucial to efficient conservation. [ ] There is little doubt that managing human-made environmental adjustments similar to noise air pollution is a crucial societal and financial problem that can finally decide the well being of ecosystems and organisms. together with folks. "
Water noise
Biology of worldwide change launched, "Sounding the alarm: a meta-analysis of the effect of water noise on the behavior and physiology of fish." The aquatic atmosphere is more and more bombarded by a wide range of noise pollution, the unfold and depth of which improve with each decade. Little is thought, nevertheless, about how water noise impacts marine communities. To decide the results that adjustments in soundscape could have on fish, a meta-analysis was carried out specializing in the results of noise on fish habits and physiology. Our meta-analysis recognized 42 research with 2,354 knowledge factors, which in flip indicated this that anthropogenic noise negatively impacts the habits and physiology of fish. The predominant reactions occurred in foraging, predation threat and reproductive success. In addition, anthropogenic noise has been proven to extend listening to threshold and cortisol ranges of quite a few species, whereas sounds, organic and environmental noise are the most probably to have an effect on advanced motion and swimming abilities. These outcomes recommend that almost all fish species are delicate to adjustments within the aquatic background noise and, relying on the supply of the noise, the reactions of the species can have excessive and damaging results on health. As such, this world synthesis needs to be seen as a warning the doubtless dire penalties that marine ecosystems face if adjustments in aquatic soundscapes proceed on their present path. "
Beaked whales
What we've not carried out on land or at sea is pay sufficient consideration to microwaves and sonar.
Whale researcher Kenneth Balcomb witnessed beaked whales stranded by the army within the Bahamas within the late Nineteen Nineties. Tomorrow we'll have a look at his ignored "resonance" discoveries. The whales warned us.
[ad_2]
Read This On Our Main Website: https://psoec.com/an-ocean-near-you-in-no-time/?feed_id=1061&_unique_id=61b035ab9a4cd

Comments
Post a Comment